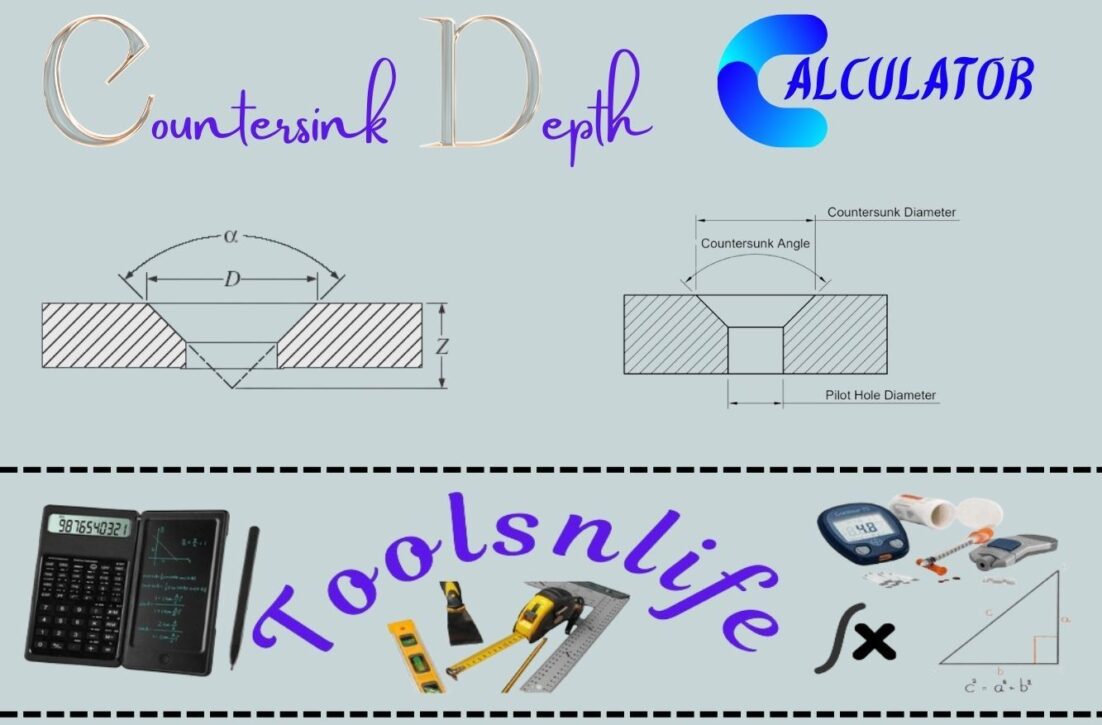
What is a Countersink Depth Calculator?
A countersink depth calculator is an essential tool for machinists, woodworkers, and DIY enthusiasts who need to create precisely angled recesses for screw heads. This specialized calculator helps determine the exact depth you need to drill to ensure screw heads sit flush with or slightly below the material surface. Unlike basic drilling operations, countersinking requires precise mathematical calculations based on the screw diameter and the angle of your countersink bit.
When I first started working in precision machining over 15 years ago, I learned the hard way that guessing countersink depths leads to costly mistakes—either screws that protrude awkwardly or recesses so deep they compromise material integrity. Our calculator eliminates this guesswork by applying trigonometric principles to deliver accurate depth measurements every time.
How to Use Our Countersink Depth Calculator
Using our calculator is straightforward, but understanding the inputs will help you get the most accurate results:
- Diameter: Enter the diameter of the screw head or the desired countersink opening. This measurement determines how wide the recess needs to be.
- Angle: Select the angle of your countersink bit. Common angles include 82° (standard for screws), 90°, 100°, and 120° (often used for deburring).
- Depth: The calculator automatically computes the required drilling depth based on your inputs.
For best results, always measure your actual screw heads rather than relying on nominal sizes, as manufacturing tolerances can vary. I recommend taking multiple measurements and using the average value for maximum precision.
The Mathematics Behind Countersink Calculations
The fundamental formula driving our calculator is based on trigonometric relationships in a right triangle:
Depth = (Diameter / 2) / tan(Angle / 2)
Here’s why this works: when you visualize a countersink, it forms a conical shape. If you slice this cone through its center, you get an isosceles triangle. The depth calculation essentially finds the height of this triangle when you know the base (diameter) and the angle at the tip.
In my workshop, I’ve verified this formula across hundreds of projects—from delicate electronics enclosures to heavy-duty structural steelwork. The mathematical consistency is remarkable, but practical factors like material compression and tool sharpness can introduce minor variations, which is why I always recommend test drilling on scrap material first.
Common Countersink Angles and Their Applications
Different countersink angles serve specific purposes in various applications:
| Angle | Common Applications | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 60° | Aerospace, thin materials | Creates shallow recesses |
| 82° | General purpose screws (US) | Most common standard |
| 90° | Metric screws, European standards | Widely used internationally |
| 100° | Aviation, specialized applications | Less common but important |
| 120° | Deburring, chamfering | Not typically for screw heads |
Through years of working with international clients, I’ve found that understanding these angle standards prevents compatibility issues. For instance, using an 82° countersink for a metric screw designed for 90° will result in an imperfect fit—something I learned during a particularly challenging international project early in my career.
Practical Tips for Perfect Countersinking
Beyond the mathematical calculation, successful countersinking requires attention to technique and tool selection:
- Use sharp bits: Dull countersinks tear material rather than cutting cleanly
- Control your speed: Higher speeds generally produce cleaner results in metals
- Consider material differences: Hard materials may require slight depth adjustments
- Test on scrap: Always verify your settings before working on final pieces
- Use depth stops: Most quality countersink tools have adjustable depth controls
I’ve developed a simple verification method over the years: after calculating the depth, I add 0.1-0.2mm to account for material compression, especially when working with woods or plastics. This small adjustment has saved countless projects from undersunk screws.
Troubleshooting Common Countersinking Issues
Even with precise calculations, you might encounter challenges. Here are solutions to common problems:
- Screws protruding: Increase depth by 10-15% or check for debris in the hole
- Countersink too deep: The angle may be incorrect—verify your bit matches the calculation
- Rough finish: Your bit may be dull or you’re using incorrect speed
- Off-center recess: Ensure your drill is perpendicular to the work surface
Remember that material matters too. When I consult on industrial projects, we often adjust calculations based on material density—softer materials like aluminum may require slightly different approaches than hardened steel.
Advanced Applications and Professional Insights
In professional settings, countersinking precision becomes critical for structural integrity and aesthetic quality. Aerospace and automotive industries often require countersink depth tolerances within ±0.05mm—a level of precision that demands both accurate calculations and expert execution.
During my time working with aerospace manufacturers, I developed specialized techniques for materials like titanium and composites, which behave differently than standard metals. The fundamental mathematics remains the same, but practical application requires understanding material-specific factors like springback and thermal expansion.
Why Our Calculator Outperforms Alternatives
Unlike basic calculators that offer limited functionality, our tool provides:
- Comprehensive unit conversion for international users
- Multiple angle measurement systems (degrees, radians, arc minutes/seconds)
- Real-time formula explanation for educational purposes
- Professional-grade precision suitable for industrial applications
- Mobile-friendly interface for workshop use
We’ve specifically designed this calculator to bridge the gap between theoretical mathematics and practical workshop application—something I found missing in most online tools during my career.
Conclusion
Accurate countersink depth calculation separates amateur work from professional results. Whether you’re a hobbyist building furniture or a machinist working on precision components, our calculator provides the mathematical foundation for perfect screw recesses every time. The combination of theoretical accuracy and practical insights gained from years of professional experience makes this tool uniquely valuable.